The national grid manages the electricity needs of the UK, making sure there is enough electricity for everyone when they need it, on a second by second basis!
Using information from a variety of sources, including television schedules, to predict what the demand will be. They work with power stations to constantly monitor demand, reacting to sudden surges such as when millions of kettles get switched on during television breaks!
Keeping an eye on these different factors means electricity is not wasted, as it cannot be stored when it’s not used. It also means the right choice of energy source (gas, wind, nuclear, etc) is made depending on the level of demand or how quickly they’re needed.
TIME OF DAY
This graph shows the changes the UK electricity demand can go through in a single day.
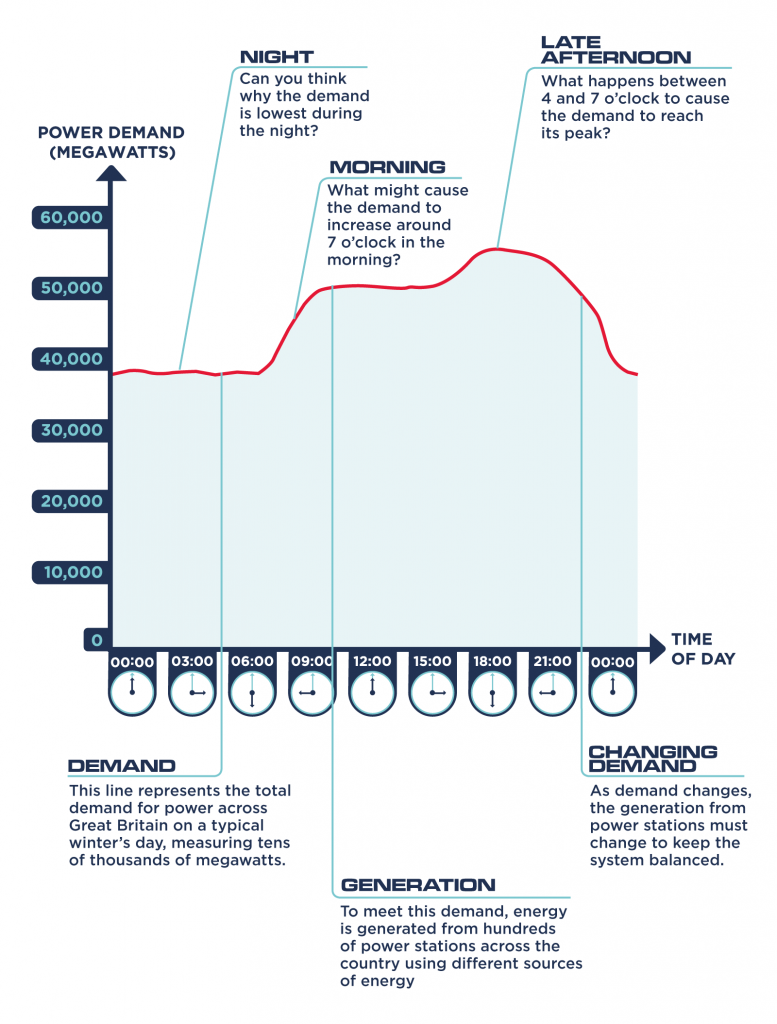
- At night, electricity demand is steady and quite low as most of the country is asleep.
- It starts to rise around 7am as people wake up for school and work; turning on lights, televisions, using showers and boiling kettles for a coffee boost!
- It then levels off as businesses and schools use a steady amount of electricity through the day for computers, lighting and heating.
- But the biggest peak happens from 3pm onwards. Any guesses on why this is? Of course you know; school is finished!
- Now people are returning home, turning on lights and televisions and preparing dinner. After this, the graph starts to drop as everyone goes off to bed, turning off gadgets, lights and things as they go.
And then it starts all over again the next day!
SUMMER VS WINTER
Electricity demand in a day does not follow quite the same pattern all year round; a winter’s day looks a little different to a summer’s day.
It’s easy to see why this would be; in summer, lighter evenings and later sunsets mean fewer lamps need to be on for a shorter period of time, activities might take place away from televisions to outdoors. In winter where light is needed for shorter daylight hours and weather may force people to stay inside and watch TV, play on computers, etc., electricity demand would be higher.
If a house uses electric heating over gas, this will also change the demand for electricity during different seasons. Winter will see spikes in demand for heating as the weather gets colder.
SPECIAL EVENTS
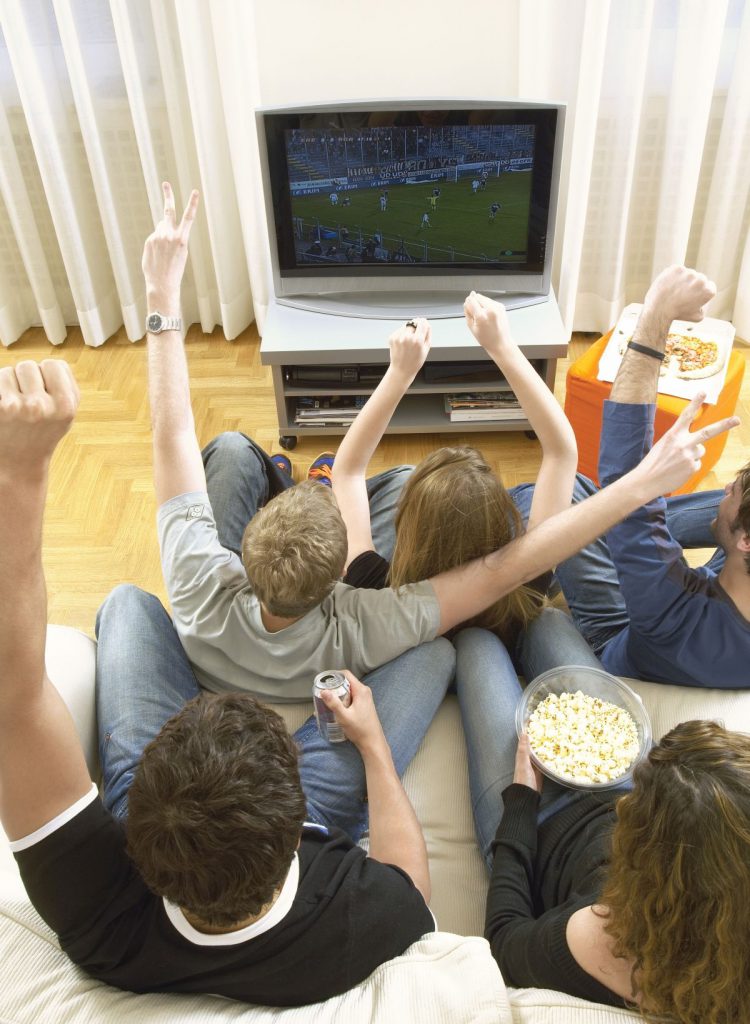

Did you know that the national grid needs to be prepared for electricity demand changes when there’s a special event on TV? Big football matches, the Eurovision final and similar special events programmes are likely to attract large audiences, so power stations are chosen accordingly depending on their characteristics.
DIFFERENCES IN ENERGY GENERATORS
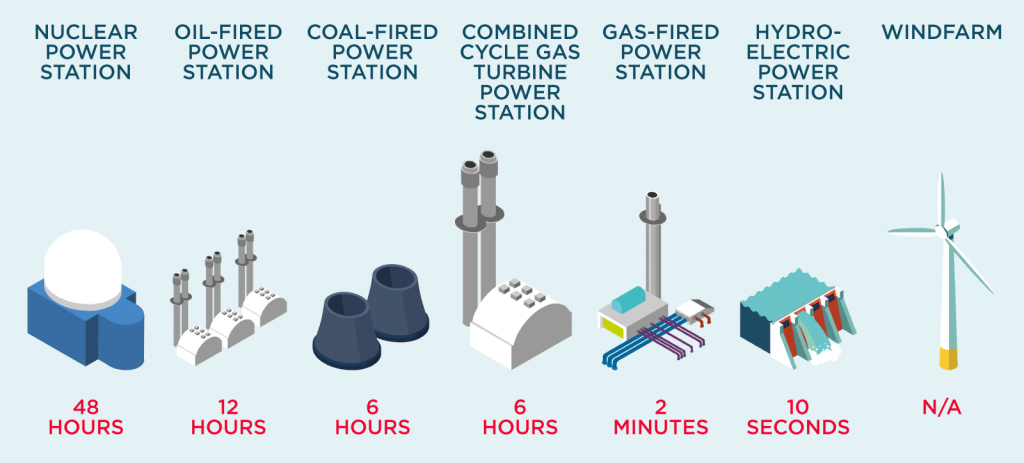
The times below each type of energy generator shows how quickly they can start-up.
Some power stations are most suited to cover gaps in electricity generation as soon as they are needed, while others are used for providing steady, base-load electricity. Base-load is the term given to the lowest level of electricity demand on an average day. Some energy generators are better at providing this, for example nuclear, which offers a continuously steady supply of electricity.
For example, nuclear takes two days to start-up and begin generating electricity. This is why nuclear power is one of the main base-load generating sources used in the UK. These stations are unlikely to be turned on and off again when once running, and are essential for consistent supply of electricity.
Hydro, on the other hand, is very flexible, only taking 10 seconds to start-up, so can be called on to meet a surge in demand when needed.
Gas fired power stations can be used for both base load and covering gaps in electricity generation, making it a very versatile electricity source.
This is an important reason as to why a varied energy mix is so important, not just to the UK, but worldwide.
Relying on one energy source can leave us vulnerable to drops in power, but by using a mix of sources, we can look at the different characteristics that make them all useful in all types of situation.












