Did you know you can tell how much energy is left in a battery just by bouncing it?!
An alkaline AA battery bounces quite high after being dropped on its end when it is empty. But when the battery is new it lands flat on its bottom with almost no bounce.
This is because the physical properties of the electrodes change when you use a battery. The anode of an alkaline battery consists of a gel-like substance. And when the battery is used the gel turns into a solid.
The unused batteries gel like substance can absorb kinetic energy, so when dropped, the gel absorbs the impact and doesn’t bounce. When the used battery is dropped the solid internal structure can’t absorb the impact but instead creates a recoil, or bounce.
Next time you change the batteries of your remote control, try it!
Anatomy of a Battery
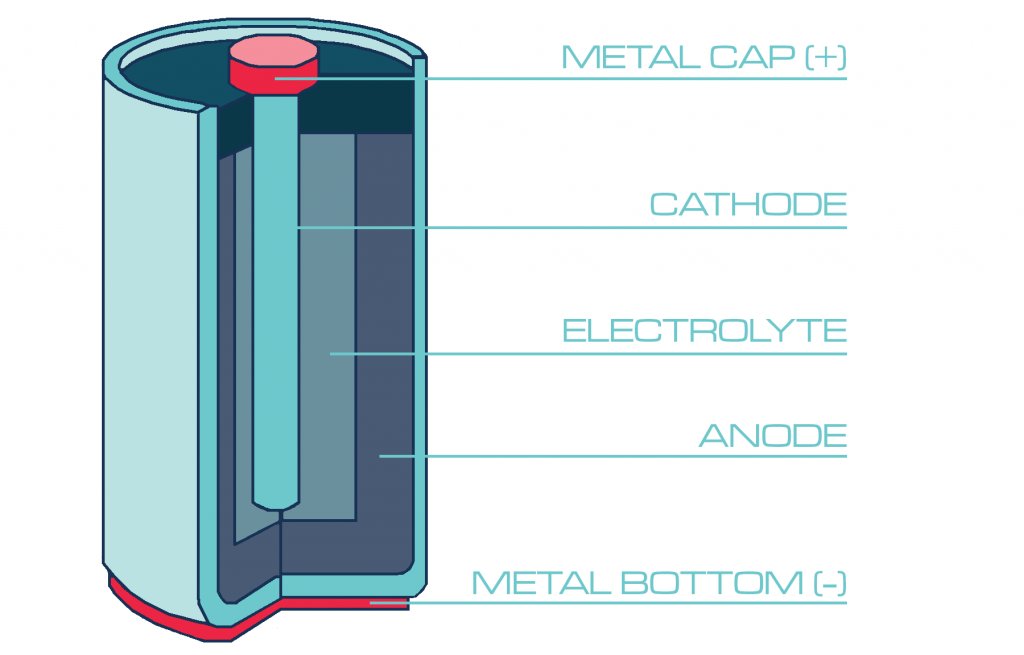
Take a look at any battery, and you’ll notice that it the ends are slightly different. One end is marked with a ‘+’ or positive, while the other is marked with a ‘-‘ or negative.
Inside the battery are a cathode and an anode.
- The cathode connects to the positive or ‘+’ end of the battery
- the anode connects to the negative or ‘-‘ end of the battery.
(Click to view full-size image)
These components, more generally known as electrodes, occupy most of the space in a battery. They are the place where the chemical reactions that produce electricity occur.
The cathode and anode are separated by a barrier that prevents the electrodes from touching, but allows electrical charge to flow freely between them. The medium that allows the electric charge to flow between the cathode and anode is known as the electrolyte.
When a battery is connected to an electric circuit, a chemical reaction takes place in the electrolyte causing an electric current to flow through the battery and the circuit it is connected to.












