No matter what time of day it is where you are, somewhere in the world the Sun is shining. So how do we harness this solar energy?
Well, we can use both the light and heat energy of the Sun as energy sources.
Light
How do we harness the Sun’s light energy?
Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert the Sun’s freely available light energy directly to electrical energy.
(click to open full-size image)
How does it work?
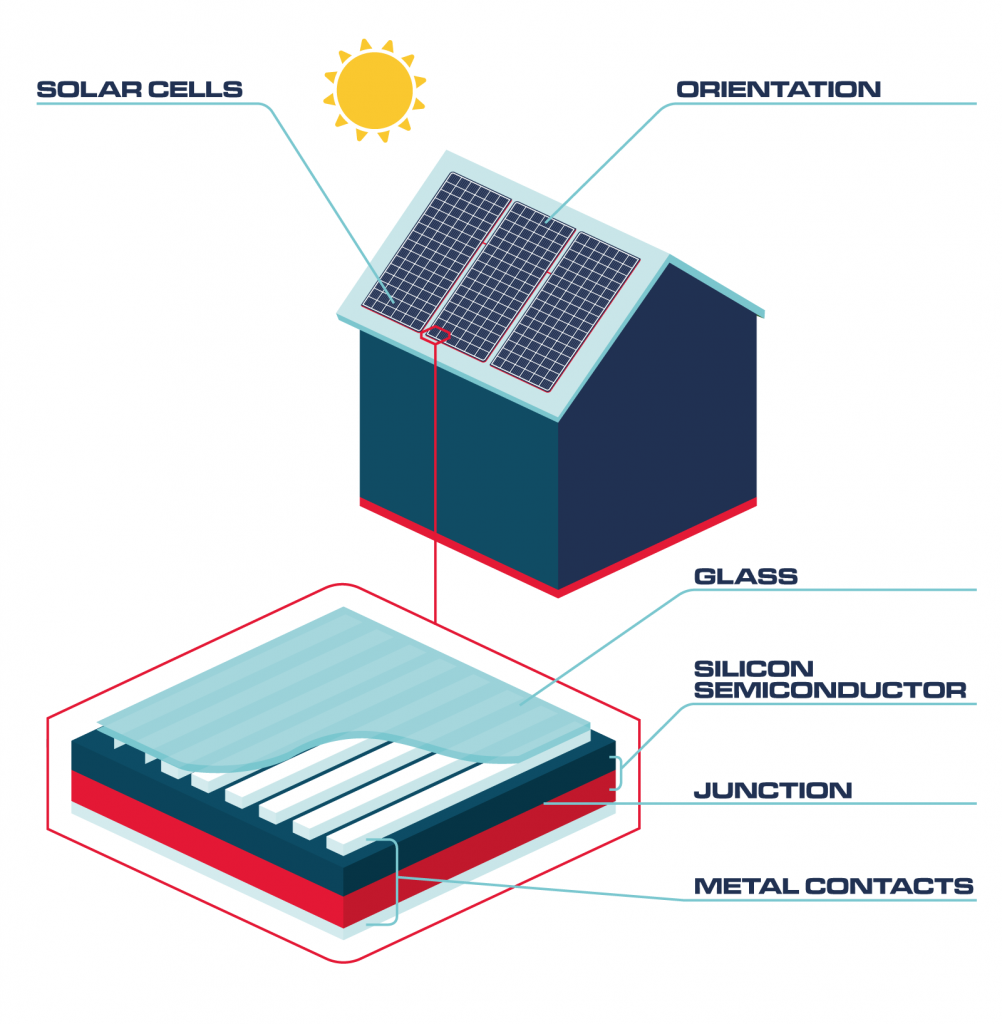
Solar panels are made up from two layers of silicon semiconductor, sandwiched between metal contacts.
To harness as much light energy as possible, solar panels should face the Sun. In the northern hemisphere, panels are installed facing south.
A layer of glass protects the solar panels and has an anti-reflective coating to stop sunlight from being reflected away. The energy from the Sun is able to knock electrons free from the silicon atoms in the silicon semiconductor, generating a flow of electricity.
A semiconductor is a material that conducts electricity at certain temperatures.
The two different layers of silicon encourage the loose electrons to flow across the junction in only one direction.
Sandwiched around the silicon semiconductor layers are metal contacts that capture the flow of loose electrons.
Solar panel installations can be as big or as small as necessary meaning that they can be fitted to rooftops, make up large solar farms and be integrated into electronic devices.
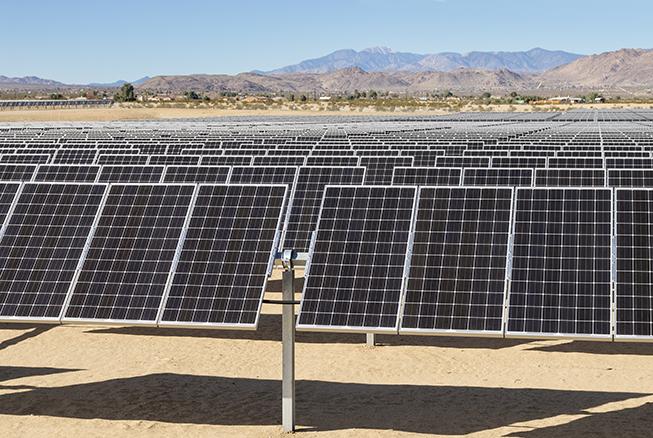

The Future of Solar Panels
Most solar panels in use today use silicon. Although silicon is abundant it is also expensive and in high demand as the solar and electronics industries compete for global supplies.
Researchers are exploring different materials and manufacturing techniques to produce new, more efficient ways of producing solar panels.












