Salt + Water = Light!
OK, so it might not be as simple as that, otherwise salt water lakes would be glowing all day every day! However, simple chemistry could provide safe and valuable light sources for those who need it most. This particular use of salt water is not new and is an example of electrochemistry.
Electrochemistry has been around for years, generating electricity from chemical reactions.
The salt water lamp is an example of an electrochemical cell. An electrochemical cell is a battery or device that can generate electrical energy from chemical reactions. This can also happen the other way around, by introducing electrical energy to start a chemical reaction, this is how rechargeable batteries are recharged.
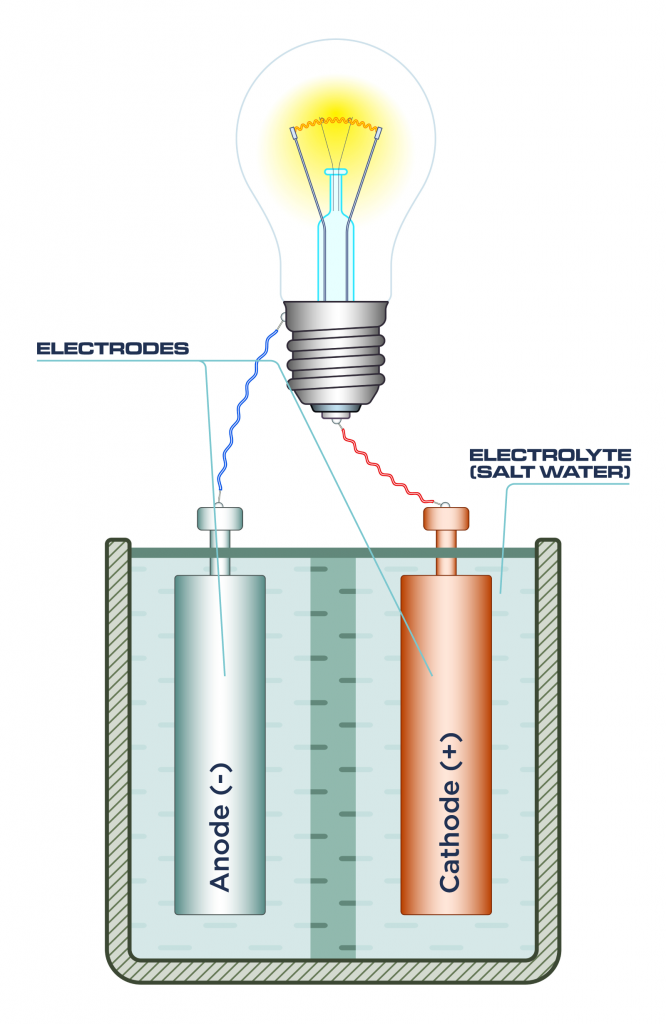
- Electrolytes are liquids that conduct electricity, in this case, the salt water found in the lamp. The electrolyte closes the circuit in the cell (or battery).
- An electrode is a piece of material that conducts electricity when it touches a non-metallic part of a circuit, i.e. the salt water in the lamp. Electrodes are often metal rods, such as zinc and copper.
- Two electrodes are found in the salt water lamp, one acting as an anode, and one as a cathode, like you would find in a regular battery.
Once the salt water is added, the circuit is closed and the battery (or cell) can power the lamp to produce light.
How Can It Help?
Inventions such as the lamp below, which use basic scientific principles, will be invaluable for areas where there is not a lot of electricity available. Having light at night means that people can work later in the evening to boost their income and children can do more homework which can greatly improve their prospects as they grow up.
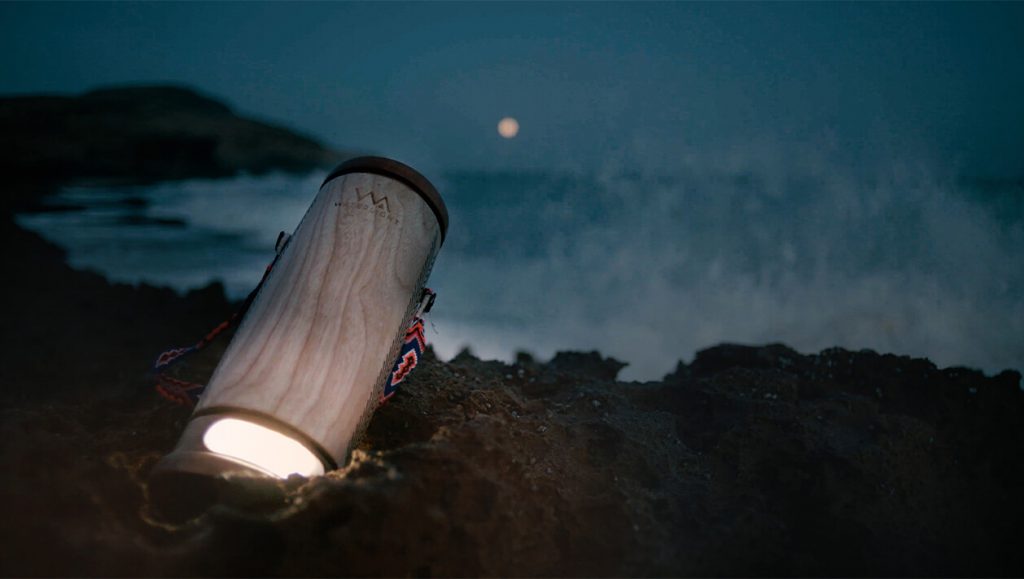

The salt water lamp above was created by E-Dina, it can use the energy generated to charge a smartphone, and in an emergency can run on urine instead of water.
There is also a safety benefit to using these lamps compared to standard kerosene or paraffin lamps. Standard lamps release fumes into the air when burning and if used indoors can be as harmful as smoking two packets of cigarettes a day. The fuel is also harmful to people and the environment if spilled and the lamps can easily start fires if dropped or knocked over.
The salt water lamp does have some drawbacks, the chemical reaction that produces the electricity erodes the anode which means it will need to be replaced after a certain number of hours. And you do need a supply of sea water or salt and water, although these are usually easy to find in most places.
But used together with rechargeable solar powered lamps, wind up lamps, and other new technologies (bioluminescence) it can provide a much safer and easy to use lighting solution for communities in developing countries.












