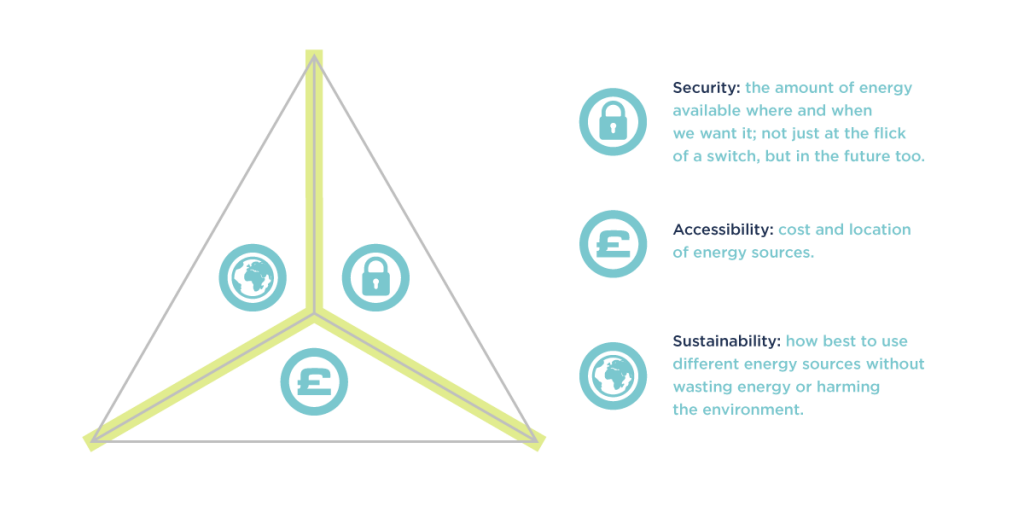
In Worldwide Energy Mix, we look at how different countries use a number of energy sources in their energy mix to provide heating, electricity and transport.
This energy mix can be judged on the country’s energy trilemma score.
The higher the country scores in each area, the better their energy mix.
CHINA’S ENERGY MIX AND FUTURE
China is home to nearly 20% of the entire population of Earth. That’s about the same number of people as 20 United Kingdoms! If this number grows at the same rate as the rest of the world, then just imagine how demand and use of energy will grow.
The country produces and uses the most energy in the world.
This might become an even bigger issue, as China already has the highest carbon emissions in the world, due to the amount of coal they burn; a problem that every country on earth is trying to prevent by phasing out the use of coal as an energy source.
However, while China is the biggest polluter, it also has the highest investment in cleaner renewable energy!
This contrast is what makes China’s energy mix and energy future one of the most interesting in the world.
Highest population
China World No.1s – Quick List
Produces, sells and uses the most energy
Largest hydropower stations
Produces, sells and uses the most coal
Highest pollution levels
Highest investment in renewable energy
Biggest coal and oil reserves in Asia
Largest solar panel manufacturer
SECURITY
Coal is the major energy source in China; the country produces, sells and uses the most coal in the world.
The exact amount of coal, oil and natural gas that China has are unknown; proven resources are already an estimate of the amount of energy available, but reports about China’s resources can already be very different, as the country is known to be quite secretive about their resources. However, their coal and oil reserves are most likely the biggest in Asia.
Large shale gas reserves in China have been found to be technically recoverable. This could mean plenty of gas to use as a source of energy while the country moves from coal to renewables; it is much cleaner, and can be used for transport, heating and electricity generation.
Hydropower is the third largest energy source, with China home to the largest hydroelectric power station in the world: The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River. In fact, China has built more than three times the amount of hydropower in the last few years than the next top five countries added together! The importance of hydropower is only set to continue, with more huge stations set to be built over the next few years.
China has around 50 nuclear reactors, Nuclear power is the country’s third largest energy source. They are also planning to export their nuclear technology and experience out to other countries, securing this energy source even further, as other countries rely on their expertise, just as they do with solar panels.
ACCESSIBILITY

China has a large and varied amount of energy sources available to them, due to the size of the country, access to plenty of water and mountains for hydro and nuclear power, as well as large reserves of coal, oil and gas.
Coal is found all over the country, and is also very affordable, making it a popular choice of energy source, despite the amount of pollution it produces.
As well as the hydropower available, which China uses to its advantage, potential for tidal energy could be big for China, as they have a number of suitable spots for tidal machines, mainly around the southern coasts.
The solar power that could be harnessed is also huge. The Gobi Desert could provide 17 TW if it was fully covered in solar panels, which is just over how much power was used across the world in 2010! Covering the full desert would be quite a challenge, but China has started work on a solar farm that covers a small part of the desert, that will be enough to power 1 million homes.
What might China’s solar farm look like?
SUSTAINABILITY

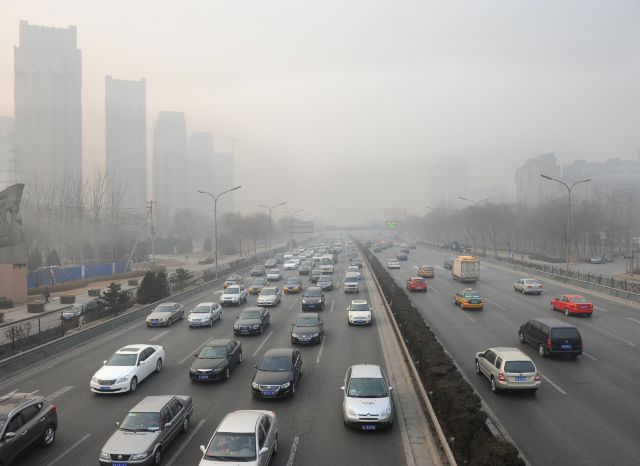
The top picture shows blue skies in Beijing as cars were ordered off the street and factories were closed for two weeks as the city celebrated a parade. The picture on the bottom shows the city one day after the celebrations ended and the city went back to normal.
China uses 50% of the world’s coal on their own! So it’s no surprise to see images like the one above. Beijing, China’s capital city is constantly on the news with images of its smog filled streets and residents wearing mouth masks as they go about their day. The air is so polluted, that people in the city are buying fresh air from Canada that is shipped over in cans!
Plans have been made to stop rising pollution levels, such as a ten-step plan to cut down coal use, as well as a deadline to stop using coal by 2020. This is likely to hit the industrial sector the worst, including steel works and construction; it could even be made illegal to go against these rules!
Despite their reliance on coal, China is the highest investor of renewables in the world, aiming to put $15 trillion into clean energy over the next 15 years, as well as encouraging companies to start working on research and new technologies for cleaner energy.
China’s energy mix in the future will depend on how quickly they reduce their reliance on coal and replace it with cleaner energy sources, of which they have already started with hydro, wind, solar, nuclear energy and natural gas.
With the size of the population, and the amount of coal available to them, this might take longer than the country, or the environment, would like…












